3. What’s required to join NATO?
The criteria include a functioning democracy based on a market economy, fair treatment of minority populations, a commitment to resolve conflicts peacefully, and a willingness and ability to make a military contribution to NATO operations. Sweden and Finland are among the world’s most developed nations, with stable democracies and highly trusted political institutions. It’s not a requirement that citizens bless a move to join, but favorable public opinion lends legitimacy to a country’s bid for membership. It also must be ratified by all existing members. Finland was approved relatively quickly and it joined on April 4, 2023, while Sweden’s bid was held up by Turkey and Hungary. Turkey finally signed off on Sweden’s entry in January, and Hungary followed on Feb. 26, after both countries clinched deals to acquire fighter jets from NATO allies.
4. How has Russia responded to Finland and Sweden joining NATO?
Russia has warned of “serious military and political consequences” that would require it to respond. In 2022, Russia said it would deploy nuclear weapons in and around the Baltic Sea region if the two joined. Lithuanian President Gitanas Nauseda dismissed the threat as “empty,” accusing Russia of already placing tactical nuclear weapons in Kaliningrad, its exclave on the Baltic. Before the Baltic states joined NATO in 2004, Russia had warned them of serious consequences, but that hasn’t materialized. On the other hand, Montenegro in 2016 said it had foiled a Russia-backed plan to assassinate then-premier Milo Djukanovic over the country’s plans to enter NATO, which happened a year later. A court in 2019 sentenced 14 people, including opposition leaders and Russian and Serbian nationals, to as many as 15 years in jail over the failed plot, though an appeals court annulled the verdicts. Before joining, Finns expected to face more spying, cyberattacks, airspace breaches and influence operations by Russia. In November, Russia began an operation of weaponized immigration, sending asylum seekers to the border and prompting Finland to close all road crossings on the demarcation.

5. How is this changing Finland and Sweden?
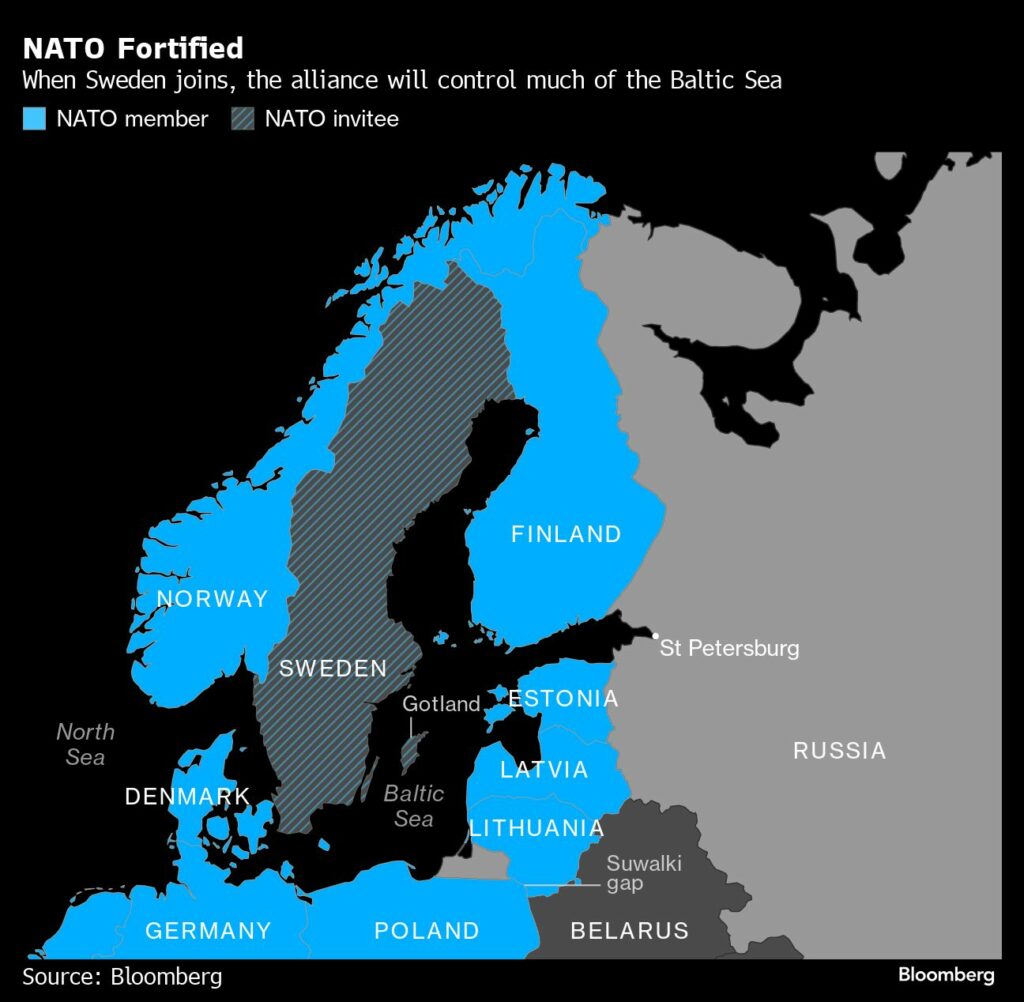
They are increasing military cooperation bilaterally and with other nations, work that began to accelerate in the run-up to the war in Ukraine. They signed defense cooperation agreements with the US in late 2023, after the US last year made security assurances to both applicants if threatened by Russia. NATO’s pledge of collective defense applies to members. They’ve also signed security cooperation agreements with the UK. They both intend to continue ramping up defense spending, with Sweden set to meet NATO’s guideline expenditure of at least 2% of national gross domestic product in 2024.
Read also:
© 2024 Bloomberg L.P.
The Reference Shelf
Related explainers on how a country joins NATO, how Russia’s invasion of Ukraine has strengthened the alliance, and why Turkey objected to Sweden and Finland joining.
The Atlantic Council looked at why Finland and Sweden can join NATO with unprecedented speed.
The Wilson Center discussed NATO membership prospects for Finland and Sweden.
Source link : https://www.biznews.com/global-citizen/2024/02/27/russia-push-finland-sweden-nato
Author :
Publish date : 2024-02-27 08:00:00
Copyright for syndicated content belongs to the linked Source.