[Getty Images]
Dorin Recean became prime minster after the resignation of Natalia Gavrilita in February 2023, having headed the government since the 2021 parliamentary election when the pro-European Party of Action and Solidarity (PAS) ousted a pro-Russian coalition.
Shortly after his nomination as prime minster, Recean named his three top priorities. “The first is discipline in government departments which must serve citizens and businesses. There is resistance to this, but we will overcome it.
“The second is breathing new life in the economy as soon as possible. This means finding more resources for investment in small and medium-size companies for them to create jobs, pay higher wages and work for our prosperity.
“The third is peace and prosperity. We must realise that we are facing the gravest threats and challenges since World War Two. We must strengthen the security sector for everyone to feel safe.”
Asked to share his vision of Moldova’s relations with Russia, Recean said: “The Russian Federation must stop the war in Ukraine. It must withdraw its troops from Ukraine. It must withdraw its troops from Moldova. Only then shall we have topics for discussion.”
Wine is Moldova’s most important export [Getty Images]
The media have changed profoundly since the 2021 parliamentary election, which brought to power a pro-European government.
The government has made it easier for journalists to access to official information, contributing to Moldova’s rise in the Reporters Without Borders media freedom ranking.
The government sees disinformation and propaganda as key challenges, as Russia continues efforts to disrupt Moldova’s European integration, retain its influence and promote parties and figures that favour close ties with Moscow.
Moldova has prohibited rebroadcasts of Russian TV news and political shows, suspended popular pro-Russian TV channels and blocked access to more than 70 Russian and pro-Russian websites.
Political battles between pro-Russia and pro-West camps are played out in the media.
Moldova’s capital, Chisinau, at dusk [Getty Images]
Some key dates in the history of Moldova:
14th-15th Centuries – Principality of Moldova stretches roughly between Carpathian mountains and Dniester river.
16th-early 19th Centuries – Moldovan territory disputed by several powers with the Ottoman Empire and Russia as the main rivals.
1812 – Treaty of Bucharest grants Russia control of eastern Moldova or Bessarabia, the area between the River Prut and the west bank of the Dniester. The Ottoman Empire gains control of western Moldova.
1878 – Ottomans recognise independence of Romanian state including western Moldova.
1918 – Following the Bolshevik revolution in Russia, Bessarabia declares independence and calls for union with Romania.
1920 – Treaty of Paris recognises union of Bessarabia with Romania. The Soviet Union does not.
1924 – Moldovan Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic established east of the Dniester River within Ukraine.
1940 – Russia annexes Bessarabia from Romania, and combines it with most of the Moldovan Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic to form Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic.
1941-1945 – Romania re-establishes control after its ally Nazi Germany invades the Soviet Union until the end of World War Two, when the Soviet Union regains control.
Late 1980s – Calls for Moldovan independence gain ground in the wake of the Gorbachev reforms in the Soviet Union.
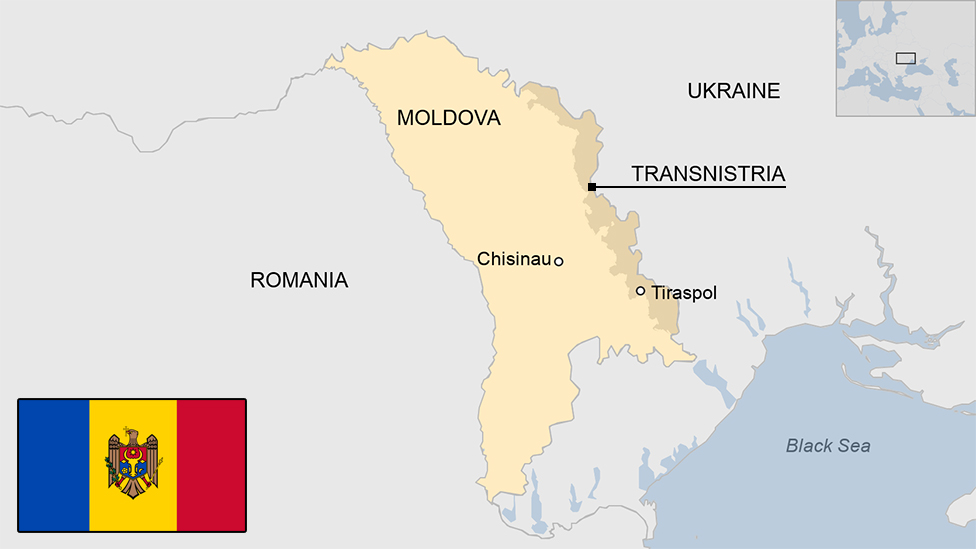
The mainly Russian-speaking Transnistria region declared independence from Moldova in 1990, sparking a conflict in which hundreds died [Getty Images]
1991 – Moldova declares independence. It joins the Commonwealth of Independent States, the successor to the Soviet Union.
Up to 700 people are killed in fighting between Moldovan and Transnistrian forces following the breakaway region’s unilateral declaration of independence.
1992 – Ceasefire signed and enforced by Russian troops already stationed in the breakaway region.
1994 – Moldova becomes a parliamentary republic.
2001-09 – Communist party returns to power in Moldova.
2006 – Transnistria referendum overwhelmingly backs independence from Moldova and a plan eventually to become part of Russia.
2009 – Three killed amid violent protests in Chisinau, following April elections which protesters claim the governing Communists rigged. In the subsequent July elections the Communists lose power.
2014 – Moldova signs association agreement with the European Union, prompting Russia to impose import restrictions on the country’s agricultural produce.
2016 – Pro-Russian candidate Igor Dodon wins first direct presidential election in 16 years.
2020 – Pro-European Maia Sandu is elected Moldova’s first women president.
2021- In parliamentary elections, Sandu’s pro-European PAS party wins a majority, defeating a coalition of pro-Russian parties.
2023-24 – US and EU impose sanctions against several pro-Russian politicians for collusion with Russia amid attempts to destabilise Moldova.
Moldova includes the autonomous region of Gagauzia, where nostalgia for the Soviet Union has been evident [Getty Images]
Source link : https://au.news.yahoo.com/moldova-country-profile-132252593.html
Author :
Publish date : 2024-10-14 15:22:00
Copyright for syndicated content belongs to the linked Source.