Key Components Influencing Habitat Connectivity and Species Survival
Habitat connectivity performs an important position in the survival and replica of species, significantly for these reliant on particular habitats, such because the Glanville fritillary butterfly within the Åland Islands. A number of key elements can considerably affect connectivity and genetic variety inside metapopulations. These embody:
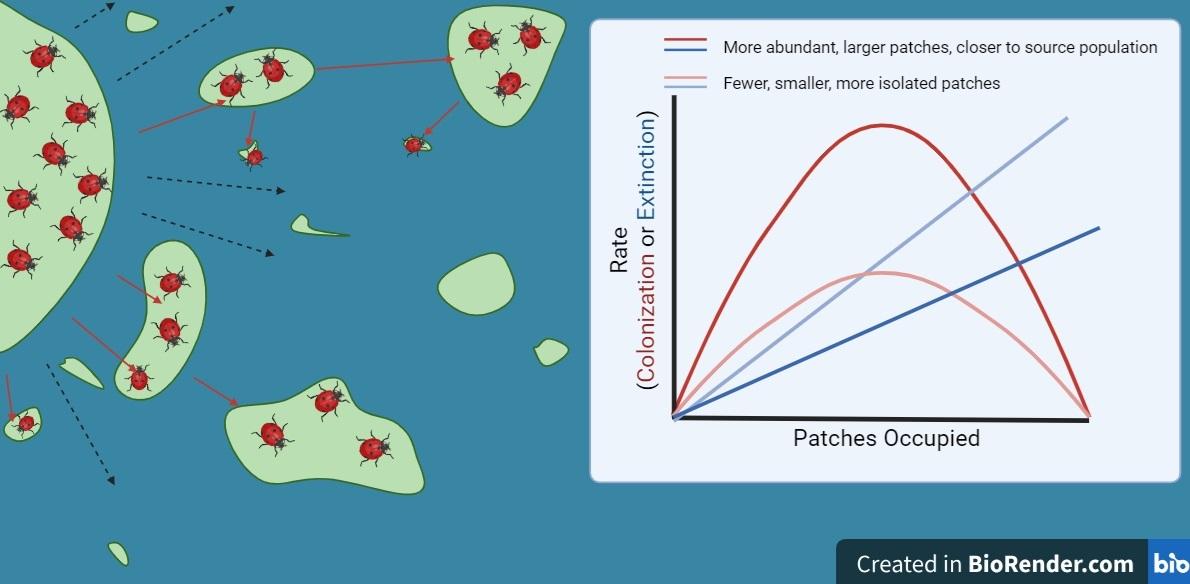
Habitat Fragmentation: The division of bigger habitats into smaller,remoted patches due to city development,agriculture,or pure obstacles disrupts motion and gene move amongst populations.Panorama Permeability: The association of environmental options can both facilitate or hinder the motion of species. Components like corridors of favorable habitat or bridges over obstacles improve connectivity.Species Conduct: The precise behavioral variations of a species have an effect on its capability to navigate fragmented landscapes. As an example, the Glanville fritillary depends on particular plant species for nectar, making habitat high quality important.
Moreover, the spatial association of populations and their respective sizes instantly influences resilience towards environmental adjustments. Key concerns on this context embody:
Inhabitants SizeImpact on SurvivalLarge PopulationsHigher genetic variety leads to improved adaptability.Small Remoted PopulationsIncreased danger of inbreeding and extinction.
Understanding these dynamics not solely aids in conservation methods but in addition highlights the significance of sustaining and restoring habitat connectivity to make sure the survival of species just like the Glanville fritillary amidst altering environmental landscapes.

The soundness of metapopulations, such as that of the Glanville fritillary within the Åland Islands, is considerably influenced by varied environmental adjustments.These shifts can have an effect on habitat availability, connectivity between populations, and breeding success, creating a dynamic interaction that may both bolster or threaten inhabitants resilience. Take into account the next elements:
Habitat Fragmentation: Elevated improvement or agricultural practices can isolate patches of appropriate habitat, impeding the motion of people between populations.Local weather Variability: Adjustments in temperature and precipitation can alter meals availability and habitat circumstances, impacting survival and reproductive charges.Invasive Species: Non-native crops and predators can disrupt native ecosystems, displacing native species and decreasing biodiversity.
Analysis signifies that the power of a metapopulation to stand up to environmental fluctuations lies in its connectivity. Populations which can be bodily linked by way of corridors are extra prone to change people,thereby enhancing genetic variety and decreasing the chance of extinction. Under is a abstract of key attributes that foster metapopulation stability:
AttributeImpact on StabilityPopulation sizeLarger sizes correlate with better resilience towards stochastic occasions.Genetic Diversityenhances adaptability to environmental adjustments.Habitat QualityImproves survival and reproductive success of people.
Conservation Methods for Defending the Glanville Fritillary in Åland
The Glanville fritillary, a placing butterfly identified for its vibrant orange and black patterns, has been a topic of concern due to its declining populations within the Åland Islands. to make sure the survival of this species, a variety of conservation methods are being applied. Key efforts embody:
Habitat Restoration: Initiatives geared toward restoring and sustaining the pure meadows and grasslands vital to the Glanville fritillary’s lifecycle.Monitoring populations: Common surveys to assess inhabitants well being and distribution, making certain well timed interventions the place obligatory.Landowner Engagement: Collaborating with native landowners by way of consciousness campaigns to promote lasting land use practices that profit the butterfly.Academic packages: Elevating neighborhood consciousness concerning the ecological significance of the Glanville fritillary and involving native faculties in conservation efforts.
As well as to those actions, the concentrate on creating a strong metapopulation framework is important. This entails enhancing the connectivity between habitat patches, enabling the butterfly emigrate and breed successfully. A current research outlines particular actions to be taken:
ActionDescriptionExpected OutcomeIncrease Meadow SizeExpand current meadows by eradicating invasive species and encouraging native flora.Improved habitat high quality and elevated meals sources for larvae.Create wildlife CorridorsDesignate pathways connecting fragmented habitats.Enhanced motion and genetic variety amongst populations.Implement Grazing ManagementControl grazing to forestall overgrowth whereas sustaining open areas for fritillary improvement.Steady inhabitants dynamics and habitat integrity.
Investigating the genetic variety inside the metapopulation of the Glanville fritillary is important for understanding its resilience to environmental adjustments. Future research ought to concentrate on:
Genomic Analyses: Implementing high-throughput sequencing methods to discover genetic variability.Translocation Research: Conducting experiments on the results of introducing genetic materials from completely different populations to boost adaptability.Pheromone Analysis: Investigating the position of chemical communication in mate choice and its influence on genetic variety.Local weather Modeling: Using predictive fashions to evaluate how local weather change might have an effect on habitat connectivity.
Equally critically necessary is integrating ecological dynamics that affect habitat utilization and inhabitants construction. Potential analysis avenues embody:
Habitat Fragmentation Results: Assessing the influence of urbanization and agriculture on motion patterns.Phenological Research: exploring the timings of life cycle occasions in relation to climatic shifts.Group Interplay Frameworks: Evaluating how interspecific relationships alter the soundness and resilience of metapopulations.Analysis FocusAnticipated OutcomesGenetic diversityEnhanced understanding of adaptive potentialClimate ImpactIdentification of vital areas for conservationHabitat UseImproved habitat administration methods

Implications for Biodiversity Conservation in Fragmented Landscapes
The research of the metapopulation dynamics of the Glanville fritillary butterfly on the Åland Islands provides vital insights into biodiversity conservation inside fragmented landscapes. Fragmentation typically leads to remoted populations, making them weak to extinction as a result of environmental stochasticity and genetic bottlenecks.Efficient conservation methods have to account for these vulnerabilities by enhancing habitat connectivity and selling habitat restoration. By implementing wildlife corridors and stepping-stone habitats, we can bolster the motion of species between fragments, in the end fostering sturdy metapopulation buildings. This strategy not solely aids in sustaining butterfly populations however additionally helps a broader spectrum of wildlife reliant on related habitats.
Moreover, understanding the particular ecological necessities of the Glanville fritillary provides a framework for focused conservation actions. Key concerns embody preserving host plant variety and sustaining panorama heterogeneity. To summarize the important conservation methods,contemplate the next:
Enhancing habitat connectivity: Implementing wildlife corridors.Restoring Fragmented Habitats: Specializing in native species reintroduction.Monitoring Inhabitants Dynamics: Common assessments and adaptive administration.Partaking Native Communities: Guaranteeing sustainable land-use practices and instructional packages.Conservation ActionsBenefitsWildlife CorridorsFacilitate gene move between populationsHabitat RestorationIncrease species richness and resilienceLocal EngagementFoster stewardship and consciousness
In Conclusion
the research of the metapopulation dynamics of the Glanville fritillary within the Åland Islands provides essential insights into the complexities of butterfly conservation and habitat administration. As highlighted within the evaluation introduced in “Determine 1,” the intricate interactions between completely different populations underscore the significance of sustaining connectivity and appropriate habitats to make sure the viability of this species. The findings not solely contribute to our understanding of the Glanville fritillary but in addition function an important reminder of the broader ecological rules at play inside fragile ecosystems. Ongoing analysis in this area stays important, because it equips conservationists and policymakers with the information wanted to develop efficient methods for preserving biodiversity in an ever-changing surroundings. As we proceed to monitor and research these populations, we’re reminded of our accountability to guard and steward the pure world for future generations.
Source link : https://europ.info/2025/03/15/aland-islands-2/figure-1-metapopulation-of-the-glanville-fritillary-in-the-aland-researchgate/
Writer : Olivia Williams
Publish date : 2025-03-15 08:35:00
Copyright for syndicated content material belongs to the linked Source.


